Electrostatic Induction
Electrostatic Induction: Overview
This topic explains concepts such as Electrostatic Induction, Charging of a Body by Induction, etc.
Important Questions on Electrostatic Induction
How can we charge a metal sphere using induction?
What is meant by electrostatic induction?
How does electrostatic induction differ from charging by friction?
What is the example of electrostatic induction?
What is the use of electrostatic induction?
What are examples of electrostatic induction?
Explain the method charging by induction with an example.
What is the purpose of electrostatic induction?
Which method involves the process in which an object is charged without actually touching the object to any other charged object - charging by conduction or charging by induction?
Charging by _____ is a method by which an object is charged without actually touching the object to any other charged object.
The electric charge generated by induction stays only as long as the charged object is near to it.
Define electrostatic induction.
What is the name of the method for charging a conductor without bringing a charged body in contact with it ?
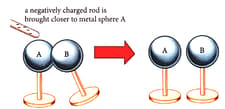
Look at the Figure, there are two metal spheres A and B touching each other. A charging rod is brought near the sphere A. What will be the nature of charge acquired by sphere A and sphere B after the process is complete?
Describe how a body can be charged by:
Induction
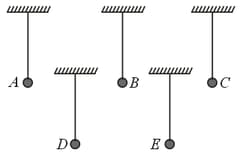
Five Styrofoam balls are suspended from insulating threads. Several experiments are performed on the balls and the following observations are made -
(i) Ball A repels C and attracts B
(ii) Ball D attracts B and has no effect on E
(iii) A negatively charged rod attracts both A and E.
An electrically neutral Styrofoam ball gets attracted if placed nearby a charged body due to induced charge. What are the charges, if any, on each ball
When a charged glass rod is brought near a charged plastic straw rubbed with polythene
Assertion: If a point charge q is placed in front of an infinite grounded conducting plane surface, the point charge will experience a force.
Reason: This force is due to the induced charge on the conducting surface which is at zero potential.
The diagram shows an earthed conducting sphere held close to a positively charged dome.
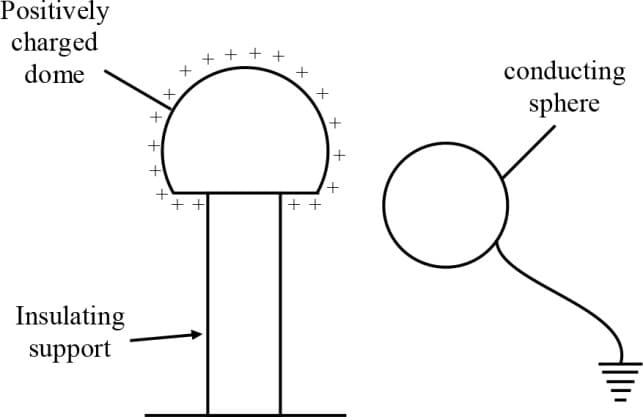
What is the charge and potential of the conducting sphere?
